INTRODUCTION
Grant funding is a critical tool that governments use to achieve their mission and provide critical services to their citizens and vulnerable populations.
In recent times, the COVID-19 pandemic and other natural disasters have increased the demand for public services. There has been a 42% increase in grants to states from the federal government between 2008 and 2019. The CARES Act alone – the federal law passed in March 2020 in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, aimed at providing economic relief and support to individuals, businesses, and various sectors of the economy – has provided $2.2 trillion in financial support.
Governments across the nation are embracing these new funding opportunities to improve service delivery. However, more funds assigned require more oversight and effort from Grant Management Offices (GMO) to ensure grant activities are adequately and effectively monitored. Tracking expenditures and activities without the tools, organizational structure, and dedicated resources to manage the funds and compliance regulations can lead to a sub-optimized allocation of said funds.
Recent research conducted on 160 government officials1 showcased that most state and local governments face challenges in managing the grants awarded due to grant management systems issues related to reporting, information sharing, interoperability, and compliance, among others.
In addition, GMOs must tackle the issues related to fragmentation of functions, lack of visibility or duplication of work to maximize funding outcomes. To overcome these challenges, governments should embrace standardization and a coordinated strategy, reimagining their approach to grants management.
This V2A insight proposes a GMO structure approach that ensures accountability and transparency of federal funds utilization. It can help governments improve responsiveness, combat fraud, waste, error, and abuse; and ensure recipients maximize grant dollars for the benefit of the public.
GMO STRUCTURE DESIGN PRINCIPLES
Grant Management Offices play a critical role in ensuring that government agencies efficiently and effectively manage grants throughout their lifecycle. They are responsible for ensuring that grants are awarded in compliance with all regulations and that the funds are used for their intended purpose. The GMO is responsible for overseeing the entire grant process, from identifying funding opportunities to monitoring the progress of grantees and ensuring compliance with regulations. This requires a thorough understanding of grant regulations, financial management, and project management skills.
The primary functions within a GMO can be grouped into four categories: Strategic, Compliance, Operational and Financial.
- Strategic functions ensure grant opportunities are maximized and federal funds are strategically aligned with public policy.
- Compliance functions ensure that the Programs are complying with all requirements of the grant and federal and local regulations.
- Operational functions ensure that grants are effectively and efficiently managed and monitored for progress and outcomes.
- Financial functions ensure adequate oversight and management of all financial transactions to optimize spending performance.
A government agency can adopt different organizational structures to manage grants, from a decentralized approach where grant management functions are distributed across multiple departments or divisions within the organization, to a centralized GMO that manages all aspects of grants within a single unit. Each configuration has its own advantages and disadvantages as seen in Figure 1.
Figure 1- GMO Structure Configurations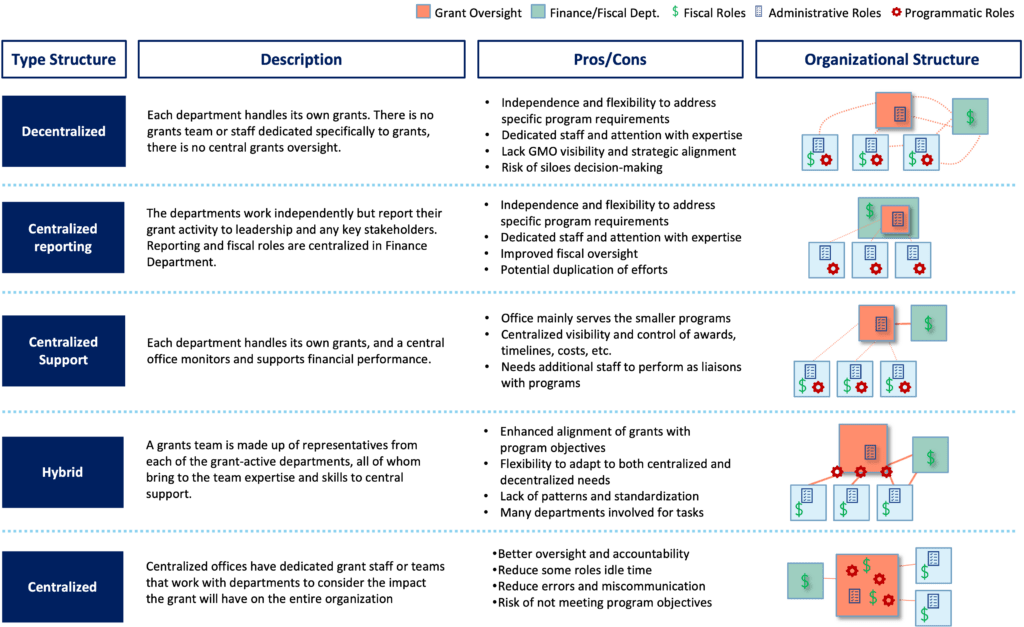
The decision to use a centralized or decentralized approach to managing grants depends on a variety of factors, such as the size, maturity and structure of the organization, the complexity and amount of grants being managed, and the specific needs and goals of the organization. However, a centralized GMO structure provides consistent and streamlined process for managing grants, that enables decision making leading to faster processing times and qualifying for more grant awards. It allows for better oversight and coordination of grant activities that increase transparency and accountability, along with improved compliance. Additionally, a centralized GMO can take advantage of economies of scale, such as shared resources and expertise, which can reduce costs and increase efficiency.
To reap those benefits, GMOs can implement a set of best practices3 in different areas.
- Standardization of policies and procedures– This makes data collection easier, reporting faster and interpretation of policies more standardized. Channeling support for policy interpretations through the GMO facilitates the sharing of those standard policy interpretations with all stakeholders through training and communication.
- Assembling the right grants management team– A high-performing GMO is achieved with close collaboration with stakeholders and the right skills and knowledge of the program needs, complemented by an advisory board with program representatives.
- Centralization of grant reporting and tools– Implementing a reporting and information collection solution enables data-driven decisions aligned with the Department’s public policy and strategies.
- Effective budget management– The centralized creation and proactive management of the budget for grant applications and technological solutions ensures cooperation and agreement among stakeholders about the budget decisions and goals to better maximize public funding.
GMO STRUCTURE OPTIMIZATION TOOLKIT
V2A was commissioned by ASTHO and the CDC to develop a GMO Structure Optimization Toolkit to guide public health agencies in implementing and sustaining a more centralized Grants Management approach to maximize federal funding outcomes. The specific project goals were to:
- Strengthen public health agency infrastructure and improve performance.
- Improve capacity to manage federal grants and funds effectively and efficiently.
- Enhance collaboration and working relationships across program areas.
The GMO Structure Optimization Toolkit includes a set of digital tools designed to conduct an annual self-assessment of federal grant workload demand, staffing needs and opportunities; recommend the best structure to manage grants workload; and allocate costs and efforts across federally funded programs.
Figure 2- GMO Structure Optimization Toolkit Overview
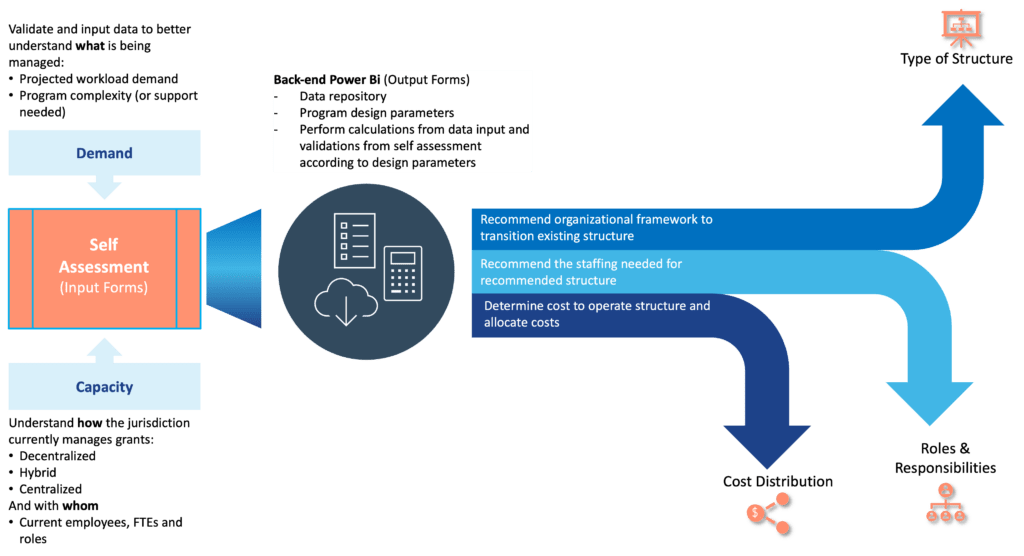
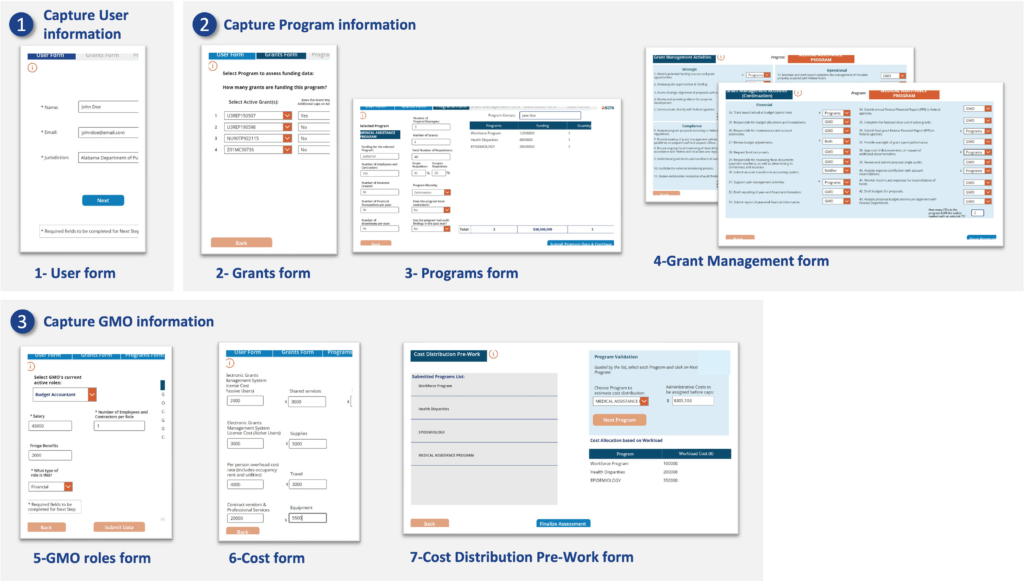
The self-assessment guides the agency through a series of input forms to capture information from 1) the user, 2) each program, and 3) the current GMO structure and costs associated with it. (See Figure 3) The workload demand of each program is analyzed in order to determine the program complexity and support needed. Additionally, each program identifies where grant management activities related to each of the functions (Strategic, Compliance, Operational and Financial) are performed, whether at the program level, centralized at the GMO level, both or neither.
Figure 3- GMO Toolkit Input Forms
The toolkit then presents opportunities to better allocate grant management activities based on the self-assessment and provides a recommended organizational framework to transition the existing one, the recommended staffing needed for such structure, the cost to operate it, and how to allocate those costs across funded programs. The outputs of the toolkit are presented in a series of PowerBI dashboards as shown in Figure 4. This self-assessment allows agencies to adequately plan their staffing needs based on the current or the projected workload to effectively manage the lifecycle of federal grants.
Figure 4- GMO Toolkit Output Forms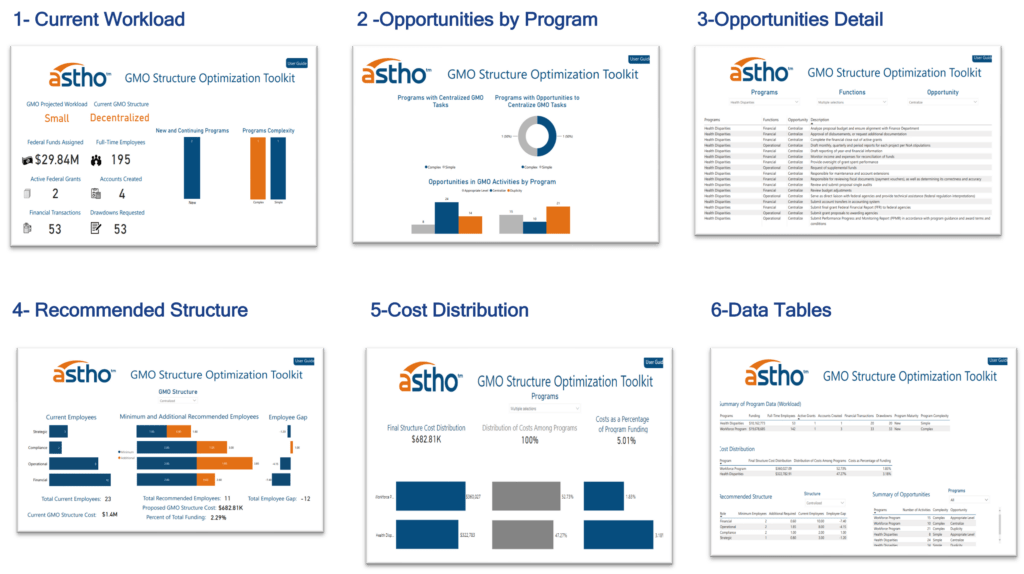
How can government agencies leverage this toolkit to optimize their Grant Management Offices?
A GMO optimization project is a three-phase effort that can be conducted with the support of V2A in collaboration with the agency’s staff.
First, a diagnostic is performed through interviews, data analysis and V2A’s self-assessment tool to understand the current state of the organization, workload demand, capacity, and cost structure. Next, the toolkit’s recommendations are shared with the agency’s staff and adjusted as necessary. Finally, a tailored implementation plan is developed for the jurisdiction to transition to the future organizational .
In conclusion, the centralization of a Grants Management Office can provide government agencies an opportunity to maximize their value delivery and funding outcomes through increased efficiency, adequate technology, and governance. V2A can partner with GMOs to support them in diagnosing their current state and visualizing opportunities using our GMO Structure Optimization toolkit and devising a transformation plan that adapts to the projected workload demand, effectively reimagining their approach to grants management.
References
1Transforming Grants Management, How Lessons from a once-in-a-century pandemic illuminate the path forward by Governing for eCivis March 2021. Research by Center for Digital Government (CDG) to 160 government officials from different agencies and departments.
2V2A Consulting fieldwork through Health Departments interviews, data analysis, coupled with eCivis Webinar: “Confessions of a Grant Writer: How to Build a Grant Team”
3How the pandemic has shaped the future of grants , GovLoop March 2021, Health Department interviews and team analysis
Disclaimer
Accuracy and Currency of Information: Information throughout this “Insight” is obtained from sources which we believe are reliable, but we do not warrant or guarantee the timeliness or accuracy of this information. While the information is considered to be true and correct at the date of publication, changes in circumstances after the time of publication may impact the accuracy of the information. The information may change without notice and V2A is not in any way liable for the accuracy of any information printed and stored, or in any way interpreted and used by a user.
ONLY ENGLISH VERSION
